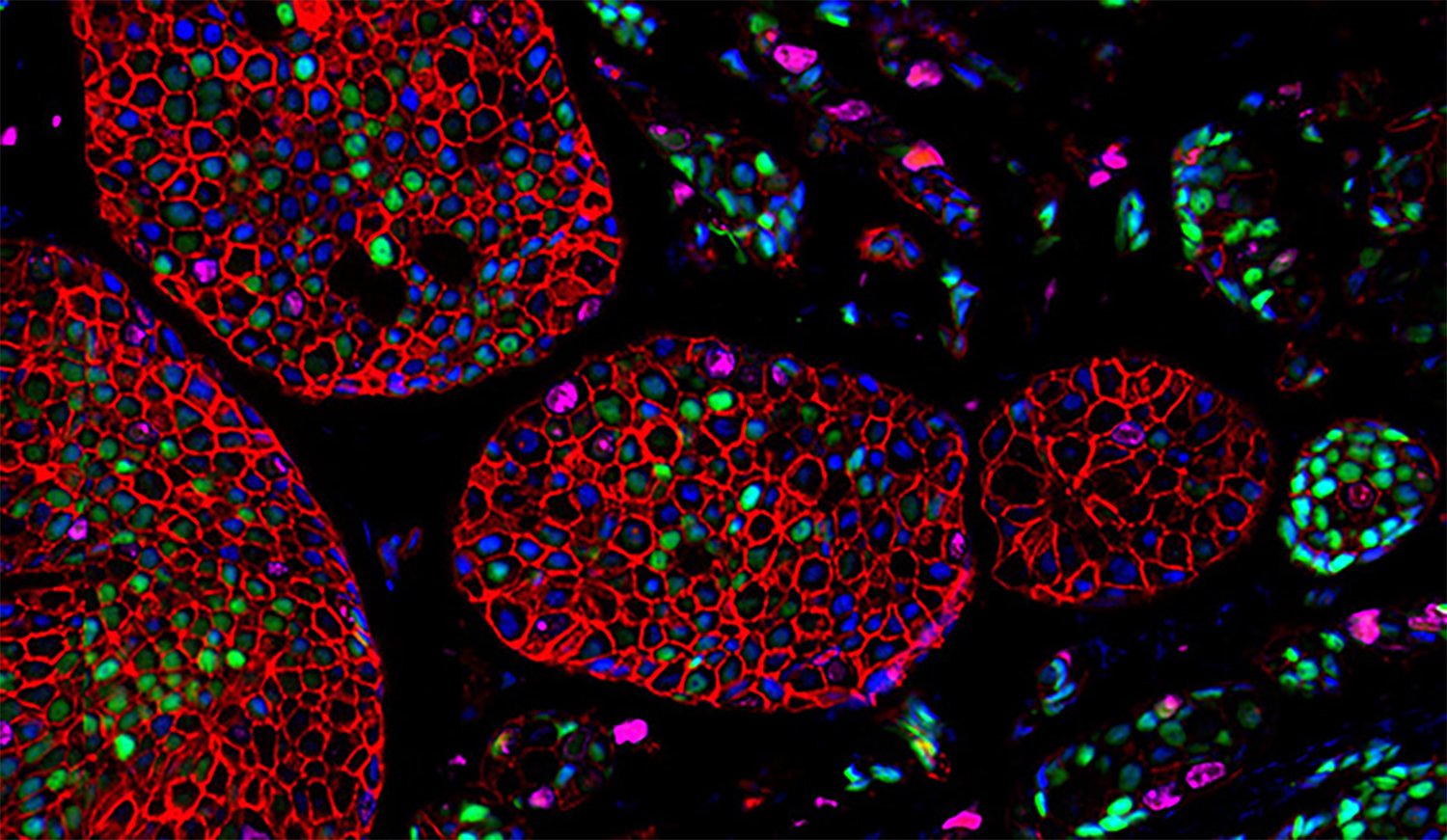
Both of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies are extensively used in IHC/IF assays. However, the staining results for a given monoclonal antibodies are quite unpredictable in different samples as compared to the polyclonal antibodies. It is very interesting to reveal the reasons underlying the performance.
We all know that it is a tough procedure to prepare IHC/IF samples, especially the paraffin-embedding samples. Chemical and physical treatments might easily destroy or block certain epitope in a target protein (antigen). As a consequence, monoclonal antibodies specific to the epitope fail to detect this antigen. In contrast, polyclonal antibodies are able to recognize multiple epitopes on the same antigen and will still recognize the target protein by binding to other epitopes. Moreover, polyclonal antibodies with good quality contain a variety of antibody molecules which recognize a series of epitopes on the antigen. When performing an IHC/IF assay, each antigen molecule will be coated by several distinguished antibody molecules. This binding property of polyclonal antibodies results in a tremendous antigen detection sensitivity and shows strong signals in the assay.
In addition, many proteins in nature have different variants. Monoclonal antibodies might not recognize all of them if the epitope is not uniformly present. This limit will interfere with the role /function characterization of the protein families. Again, the feature that polyclonal antibodies recognize multiple epitopes, they tend to be less affected by such variations and show better sensitivity of antigen detection in the IHC/IF assay.
Taken together, due to the overall detection sensitivity, experienced scientists prefer to use polyclonal antibodies in IHC/IF assays, rather than monoclonal antibodies.
Bioss supplies validated polyclonal antibodies in support of research and many of them have been reported in scientific journals.
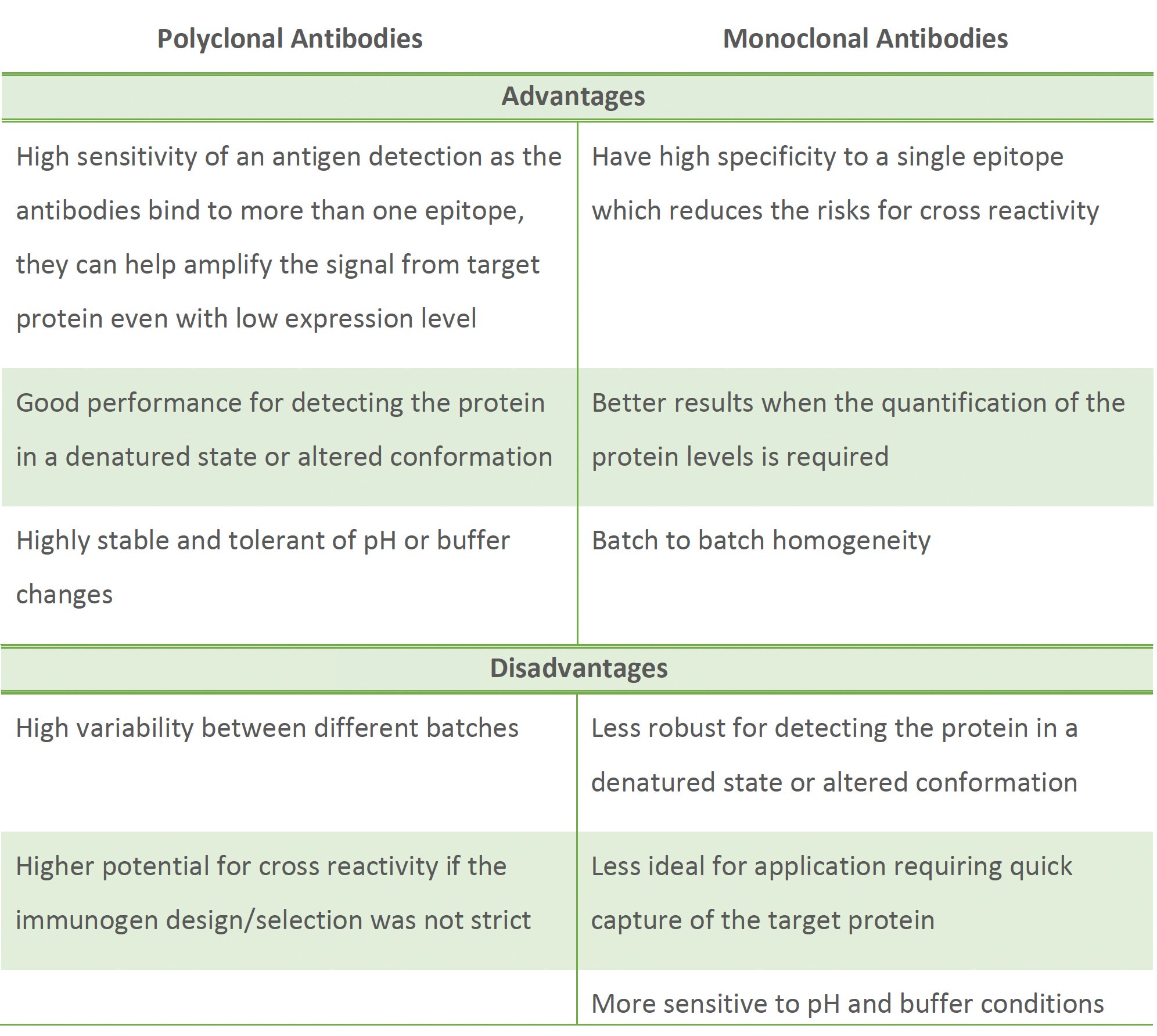
Despite the previous discussion, many good monoclonal antibodies performed very well in a given IHC/IF application. Therefore, when deciding between the use of a monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies, the essential consideration should be the conditions and aims of your experiments. Below we have summarized some of the more distinct advantages and disadvantages presented by each type of antibodies.