Systemic lupus erythematosus is a chronic autoimmune disorder that can affect nearly any organ system in the body. A common symptom is lupus nephritis, which occurs when the disease attacks the kidneys causing inflammation, one of the leading causes of morbidity and mortality amongst lupus patients. In a recent study, researchers from the University of Houston, Texas, and Tongji University School of Medicine, Shanghai, investigated whether antagonism of the bradykinin receptor B1R ameliorated this symptom.
Bradykinin is a small peptide that is involved in regulating inflammation throughout the body. Its primary function is as a vasodilator; it is also involved in the activation of the innate immune response.
Two receptors, B1R and B2R, mediate bradykinin signaling. B1R is expressed at sites of inflammation and drives inflammatory processes, while B2R is constitutively expressed and appears to have an anti-inflammatory effect. Indeed, antagonism or deletion of B1R improves symptoms of other kidney diseases including glomerulonephritis and acute kidney inflammation, whereas B2R antagonism worsens nephritis.
In the current study, investigators used a mouse model of lupus in which disease results from an overproduction of immune cells. Using the Bioss rabbit anti-mouse B1R antibody (bs-8675R) and rabbit anti-mouse B2R antibody (bs-2422R), the team observed both by Western blotting and immunohistochemistry that lupus-prone mice expressed double the amount of renal B1R and lower levels of renal B2R compared to wild type mice, signaling inflammation in the kidneys of the lupus-bearing mice.
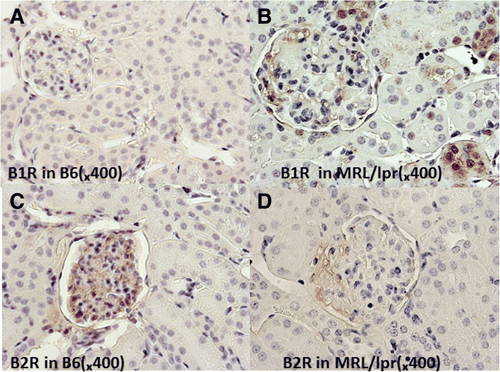 Figure 2 from the study in Arthritis Research and Therapy demonstrates by IHC-P staining the increased presence of B1R and decreased presence of B2R in the renal tissue of lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice.
Figure 2 from the study in Arthritis Research and Therapy demonstrates by IHC-P staining the increased presence of B1R and decreased presence of B2R in the renal tissue of lupus-prone MRL/lpr mice.
The researchers then used the small molecule inhibitor SSR240612 to antagonize B1R in 4-month-old mice with lupus. Systemic lupus symptoms such as total serum IgG, ratio of kidney weight to body weight, and IgM and IgG anti-histone autoantibody levels, were all lower in treated animals.
Blocking B1R also significantly decreased two measures of kidney damage: proteinuria, or protein in the urine, and blood urea nitrogen (BUN) levels. Decrease in glomerular sclerosis, a scarring of the functional units of the kidney, was observed 12 weeks following the initiation of treatment. These results indicate that B1R blockade can improve both systemic lupus symptoms as well as those associated specifically with lupus nephritis.
Since lupus is an autoimmune disorder, the researchers next investigated the impact of B1R blockade on cytokine and immune cell levels. Mice with lupus that were treated with SSR240612 exhibited significantly lower levels of immune cells in the spleen and kidney compared to their untreated littermates, including B cells, helper T cells, macrophages, and myeloid derived suppressor cells, which are commonly dysregulated in lupus. Treated mice also excreted lower levels of CCL2 and CCL5 in the urine and had a lower level of these proteins in the kidneys. CCL2 and CCL5 expression were previously reported to be regulated by B1R and have been implicated in lupus nephritis pathogenesis.
Because B1R blockade has now been shown to functionally alter the immune system in mice with lupus nephritis and improve several common symptoms of the disease, researchers may look to B1R antagonists as potential candidates for therapeutic development.
View related Bioss products for investigating the bradykinin pathway
| CATALOG |
NAME |
APPLICATIONS |
SPECIES |
| bs-8675R |
B1R Polyclonal Antibody |
WB, IHC-P, IF(IHC-P) |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
| bs-2422R |
B2R Polyclonal Antibody |
WB, IHC-P, IF(IHC-P) |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
| bsm-54224R |
B2R (4C5) Monoclonal Antibody |
WB, FCM |
Human, Mouse |
| bsm-52512R |
Ku80 (1F1) Monoclonal Antibody |
WB, IF(ICC), IHC-P |
Human |
| bsm-52970R |
Ku70 (6D1) Monoclonal Antibody |
WB, IF(ICC), IHC-P |
Human |
| bsm-50261M |
Kininogen precursor (24F9) Monoclonal Antibody |
WB |
Human |
| bsm-52596R |
ATG5 (4G5) Monoclonal Antibody |
WB, IF(ICC), IHC-P |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
| bs-2716R |
TLR6 Polyclonal Antibody |
WB, FCM, IHC-P, IF(IHC-P) |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
| bsm-52938R |
TNF Receptor II (7D3) Monoclonal Antibody |
WB, FCM, IHC-P, IF(IHC-P) |
Human, Mouse, Rat |
| bsm-52938R |
CXCL5 Polyclonal Antibody |
IHC-P, IF(IHC-P) |
Mouse, Rat |
References
Qin, L., Du, Y., Ding, H., Haque, A., Hicks, J., Pedroza, C., Mohan, C. (2019). Bradykinin 1 receptor blockade subdues systemic autoimmunity, renal inflammation, and blood pressure in murine lupus nephritis. Arthritis Research & Therapy, 21:12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1774-x