COVID-19 is the infectious disease caused by a novel coronavirus, which was first identified by Chinese authorities and provisionally named as 2019-nCoV. The International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses gave the official name SARS-COV-2 to the novel coronavirus shortly after. SARS-COV-2 has a close genetic similarity with SARS-CoV, the other viral agent identified from another coronavirus outbreak in 2003. From the previous epidemic, we learned that the rapid and widespread point-of-care (POC) testing is the foundation to curb the coronavirus pandemic.
“So far, the frontline response to the SARS-CoV-2 outbreak has been polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing. PCR is the gold standard for diagnosing an infectious agent, and it has the advantage that the primers needed for such tests can be produced with relative speed as soon as the viral sequence is known.” An article that was first published on March 24, 2020, mentioned. Currently, large providers such as Roche Diagnostics, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Qiagen (soon to be acquired by Thermo Fisher), and Quest Diagnostics are ramping up the capacity to perform such tests by rolling out automated SARS-CoV-2 testing systems and services.
Notably, the PCR test is complicated and expensive and is mainly suited to large, centralized diagnostic laboratories. Tests typically take 4–6 hours to complete, but the logistical requirement to ship clinical samples means the turnaround time is 24 hours at best. To accelerate COVID-19 testing, immunoassays based on antibody-antigen recognition drew public health authorities’ attention. Either by using cloned viral antigens to detect patient antibodies directed against the virus or by using monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to detect viral antigens in clinical samples, immunoassays can provide historical information about viral exposure, as well as diagnostic evidence.
Berlin-based Pharmact has designed a 20-minute immunoassay to detect any patient antibody that recognizes three SARS-CoV-2 antigen proteins: the nucleocapsid (N) protein and the S1 and S2 domains of the spike (S) protein. This assay detects both immunoglobulin (Ig) M and IgG antibodies, which are released during the initial and later stages of an infection, respectively. It has conducted validation studies that compared its test with PCR, using samples from 114 infected patients and 126 uninfected controls. The test obtained zero false positives, indicating the perfect assay specificity. However, its sensitivity was lower, as the IgM response does not offer a strong initial signal. During the early stage of the infection (days 4–10), the IgM component of the test provides a sensitivity of just 70%. This rises rapidly to 92.3% between days 11 and 24, and the IgG component of the test offers a sensitivity of 98.6% during this phase of the infection. Overall, the test has a false-negative rate of 13%.
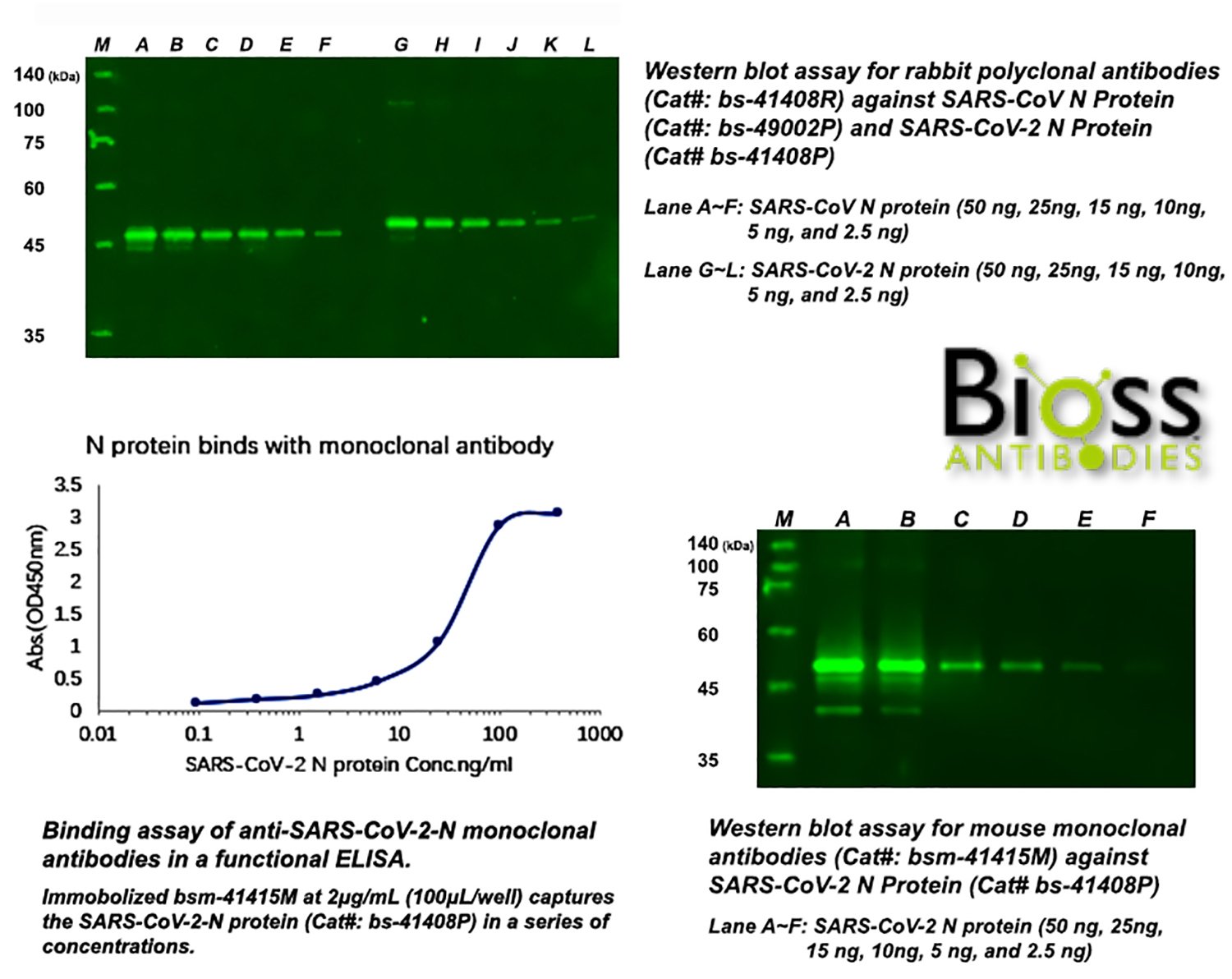
In parallel to tests to detect polyclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 in patients, the other immunoassay is to detect the virus itself. A research team in Taiwan claimed to be first to develop a mAb against the N protein of SARS-CoV-2, which could form the basis of a rapid antigen test. Sona Nanotech, in cooperation with GE Healthcare Life Sciences, is also working on the assay development by targeting the S1 domain of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. If successfully manufactured and validated, the rapid immune-based test kit could detect coronavirus antigen in only 20 minutes without instrumentation and trained personnel. Although the immunoassay is less accurate compared to PCR test, its speed and versatility make it an invaluable test, and efforts to produce them on a massive scale are beginning to ramp up.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Reference
Fast, portable tests come online to curb coronavirus pandemic. 23 March, 2020. Nature Biotechnology doi: 10.1038/d41587-020-00010-2
